Cloud computing touches us all. There’s an explosion of cloud-based applications and services. Click here to learn the basics of private, public, and hybrid cloud.
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, the term cloud computing is often encountered in a variety of contexts, from business operations to personal technology, yet the concept remains elusive for many. How it works and its file rendering can provide valuable insights to individuals and organizations alike. To provide a comprehensive review.
Definition of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing refers to the provision of computing services, such as service history, data, networking, software, analytics, over the Internet or in the cloud or perspective, without the physical need for resources and applications that can be accessed and managed remotely. By leveraging the cloud, individuals and businesses can achieve greater efficiency, scalability and cost-effectiveness in their computing needs.
Evolution of cloud computing:
To appreciate the current state of cloud computing, it is useful to understand its origins. The concept has its roots in the 1960s when computer scientists envisioned a future where computing power could be provided as a public utility. It wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s that technological advances made cloud computing a practical reality, with companies such as Amazon Web Services, AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure introducing advanced download speeds. What has since become integral to the digital economy.
The basic components of a cloud company:
Cloud computing can be divided into several core components that work together to provide computing services in an accessible manner.
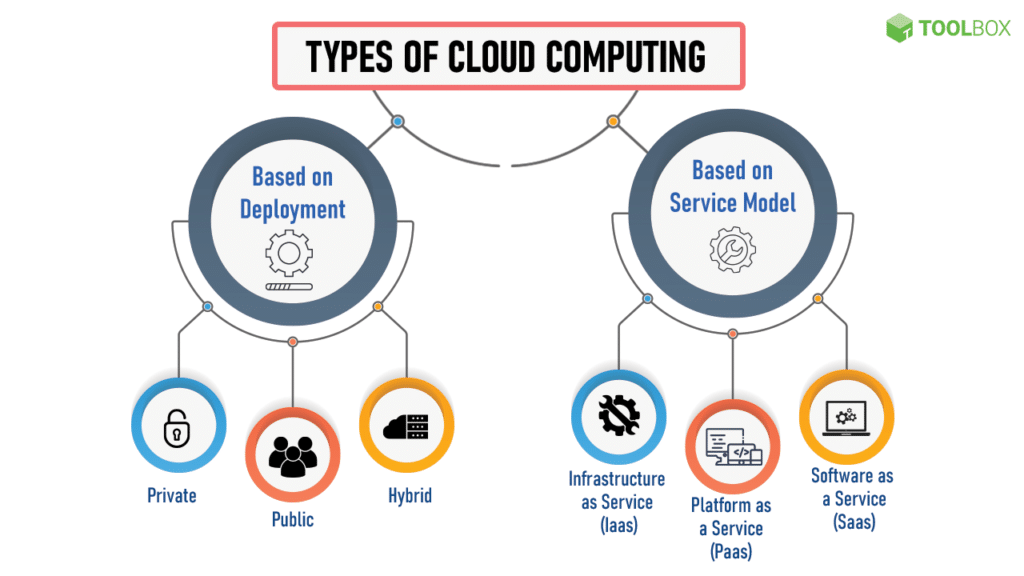
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
It provides centralized computing resources on the Internet. It offers basic services such as cloud machine storage and networking. All fans and resources can be rented on a pay-per-use basis. KC to Google Complete Engine and Microsoft Azhar Virtual Machines are included.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Pass offers a platform that allows developers to create, deploy, and manage application connections without worrying about infrastructure. It includes tools and services for application replication, such as database modules, modules and development Examples of Framework Pass include Microsoft Azure App, Google App Engine Services, and hroquo.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS subscription-based software provides Appli connections over the Internet, eliminating the need for location installation, memory, and deployment. Servers access Appli connections through a web browser. Force included.
4. Function as a Service (FaaS)
Also known as Faas-like Services and Laced Computing, Sarfin enables managed services to execute code without responding to units. Google Cloud Functions, AWS Lambda and Azhar Functions are notable Faas-offerings.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models:
Cloud computing is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it can be deployed in various models to meet different needs and preferences.
1. Public Cloud
In the public cloud model, services are provided over the Internet and shared between committed organizations or individuals. Public clouds are managed by third-party cloud service providers and offer skill flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Includes Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.
2. Private Cloud
A cloud is dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on them by third-party providers. It offers better security and control, but can involve higher costs than public clouds. Specific regulatory requirements by businesses are used here with security requirements.
3. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Clouds leverage public and private cloud elements, allowing organizations to use a mix of on-premises and cloud-based resources. This model provides flexibility and flexibility to balance workloads between organizations and public environments. Enables hybrid cloud is critical for businesses with demanding needs such as leveraging public cloud resources for other tasks while handling sensitive beta internally.
4. Community Cloud
A community cloud is shared among multiple organizations with similar interests or needs, such as industry-specific regulations. It is often managed by one of the participating organizations or by a third-party provider. Community clouds can be beneficial for compliance with industry standards.
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing offers a multitude of benefits that can transform how organizations and individuals approach their IT needs. Here are some of the most significant advantages.

1. Cost Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of cloud computing is its cost efficiency. Traditional IT infrastructure requires significant investments in hardware and software, as well as ongoing maintenance costs. Cloud computing, on the other hand, is a PSU model. This allows the entire train to pay only for problems that consume the resources or resources it presents, reducing costs and eliminating the need for large capital expenditures.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing provides unprecedented scalability and flexibility. Servers can quickly scale up or down resources based on demand, ensuring they only use what they need. But valuable for businesses with fluctuating or seasonal workloads, the larger cloud service offers a range of options to meet a variety of needs, from small-scale appreciable connections to large enterprise solutions.
3. Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud computing enables users to access apps and data from anywhere with an Internet connection. This increased access facilitates remote work collaboration and global collaboration. Team members work on shared documents in virtual meetings. can participate and access project data from their location, promoting greater collaboration and productivity.
4. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud computing enhances disaster recovery and business continuity efforts. It can be restored immediately in the event of a disaster.It reduces the risk of data loss and minimizes downtime.
5. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud service providers manage their infrastructure and app updates, ensuring that customers always have access to the latest features, security patches, and performance improvements. This eliminates the need to manage and maintain apps, allowing them to focus on their core activities.
6. Enhanced Security
Although security services are often associated with cloud computing, many cloud providers implement strong security measures to protect data and applications, including encryption access controls and regular security audits. Those often have security teams and the time resources that an individual organization can afford to implement on their own.
7. Environmental Sustainability
Cloud computing can contribute to environmental sustainability by optimizing resource utilization and reducing energy consumption. And the overall carbon footprint can be lower than that of a traditional in-premises data center.
Cloud Computing Use Cases:
The versatility of cloud computing allows it to be applied across various industries and scenarios. Here are some common use cases:
1. Data Storage and Backup:
Cloud storage provides a cost-effective way to store and back up any data. Individuals and businesses can use cloud storage to securely store files, documents, and media across multiple devices. With the added benefit of accessibility.
2. Web Hosting:
Cloud computing is used at the right scale for web hosting, which provides the infrastructure needed to host websites and applications. makes an attractive option for.
3. Application Development and Testing:
Developers use cloud platforms for testing and implementation while building applications. Cloud-based development environments offer flexibility, scalability, and access to widely trusted tools and services, streamlining the development process and improving time-to-market.
4. Big Data and Analytics:
Cloud computing enables organizations to analyze large amounts of data using powerful computing resources. Cloud-based commercial platforms provide tools for data processing visualization and visualization, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and drive value. It helps in detecting menstruation.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Cloud platforms offer a range of AI and machine learning services that allow organizations to develop and deploy mind-applied connections. These services include pre-built models, training tools, and computational resources. It makes it easy for businesses to leverage AI technology.
6. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Cloud-based CRM systems such as Salesforce and HubsForce help businesses manage customer interactions, track and analyze customer data, contact management, leadership, and automated marketing to enhance customer relationships. and offer features such as driving development.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits that have made it a transformative technology across industries. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Savings:
One of the most compelling reasons for adopting cloud computing is the potential for cost savings over traditional IT infrastructure that requires hardware, software licenses, and significant upfront capital or spending caps for data centers. Cloud computing shifts these costs to operational costs hopax, where organizations pay for resources on a subscription or usage basis such as pay-as-you-go.
Allows for scaling over time In addition to reducing capital costs, cloud computing reduces operational costs associated with managing and maintaining hardware, such as cloud provider service maintenance, security, app updates, and system monitoring. This allows IT teams to focus on more structured initiatives.
2. Scalability and Flexibility:
Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility, whether a business is growing rapidly or experiencing fluctuating demand. The cloud allows streamlining of resources to meet changing needs. Valuable for those experiencing seasonal growth or for startup apps that need to scale quickly without investing in new hardware.
Computing power without the delays and costs associated with traditional cloud computing. This flexibility extends to software development. Developers can quickly spin up new environments, test applications, and deploy updates. Time to market may be short.
3. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
Disaster recovery is an important aspect of any organization’s IT strategy. Cloud computing offers a built-in disaster recovery solution that allows organizations to back up and replicate data to remote locations and in the event of a disaster. Ensures business continuity Cloud-based disaster recovery is often more cost-effective than traditional disaster recovery plans that require maintaining physical backups and hardware at cloud providers.
Cloud providers typically have multiple data centers spread over different geographic regions to provide redundancy and reduce the risk of data loss in the event of a hardware failure or natural disaster in one data center. Can redirect to another data center to reduce downtime.
4. better collaboration and mobility In today’s:
increasingly remote and mobile work environment, cloud computing plays a greater role in optimizing productivity and productivity. Tools such as Google Workspace, Microsoft Teams and Select allow teams to collaborate on documents, share files, and real-time. It allows communication regardless of their physical location or increases productivity and ensures that team members are always connected even when working remotely or in different time zones.
5, security and education Security:
A major concern for organizations moving to the cloud, but cloud providers have made significant strides in ensuring the security of data and applications. Data encryption multi-factor authentication invests heavily in MFA and firewalls They also employ dedicated security teams that monitor and troubleshoot potential threats In addition to security, cloud providers provide a variety of services.
Offer compliance certifications ensuring that businesses can meet regulatory requirements for data privacy and security.For organizations handling.
6. Environmental Sustainability:
Cloud computing contributes to environmental friendliness by reducing the need for energy-intensive IT infrastructure. Reduce your carbon footprint by using techniques to optimize workloads and use shared resources.Cloud computing reduces overall energy consumption, helping organizations reduce their environmental footprint.
Many cloud providers are also committed to the principle of carbon-neutral or carbon-neutral appliances, promoting sustainability in the tech industry and increasing awareness for businesses looking to improve their energy efficiency efforts. It can be an effective way to reduce costs.
7. Competitive Advantage:
Cloud computing can give businesses a competitive edge by improving agility, flexibility, and agility. Cloud-based platforms allow businesses to quickly develop products, test services, and test products without the limitations of traditional IT infrastructure.
This speed-to-market can be critical in industries where continuous innovation is required to stay ahead of the competition. This democratization of technology would allow small companies to compete on an equal footing with larger competitors by leveraging cloud-based tools and services.
8. Automation and AI Integration:
Cloud platforms are increasingly integrating automation and artificial intelligence capabilities, allowing businesses to streamline operations, improve processes and make decisions based on data. AI and machine learning services in the cloud Vast amounts of data can be used to identify patterns and automate routine tasks.
For example, cloud-based e-tools allow businesses to improve customer service through chatbots and chatbots. Can help enhance marketing strategies with predictive prioritization and improve supply chain management with real-time visibility. helps organizations reduce manual efforts and improve efficiency.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way business data is accessed, stored and managed. Its benefits range from cost savings and scalability to improved collaboration and security, making it a powerful tool for modern enterprises. Create tools As more organizations embrace the cloud, its role in enabling digital transformation and fostering global connectivity will grow, whether you’re a small business that scales in a way or a large enterprise that can Looking to optimize IT infrastructure, the cloud offers the flexibility, power and resources needed to stay competitive in the fast-paced world of beauty.

