Its Computer Hardware Components, on the other hand — in essence computer hardware elements courtesy of the various permutations they have gone through reaching their modern forms—these are woven so deeply into what is now considered daily life that without them personal communication to global commerce would be impossible.
Beneath the surface, these workhorse devices are actually a group of computer hardware components that collectively perform multiple functions in order to process complicated tasks quickly and efficiently. Fundamentally, learning how computers work requires you to understand the parts of a computer and what they do. In this article, we elaborately discuss the Computer Hardware Components along with their function as well as how various components are interconnected and figure out their importance in overall system operations.
Computer Hardware Components Table of Contents.
- Computer Hardware Components Introduction
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory: RAM and ROM
- Storage Devices
- Motherboard
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Input Devices
- Output Devices
- Peripheral Devices
- Networking Hardware
- Conclusion

1. Computer Hardware Components Introduction.
Computer — It is an electronic device capable to perform a number of tasks through processing information. It has both the hardware and software of a computer. Computer Hardware Components refers to the physical components that make up a computer, and software contains instructions on what hardware will do when perform an action. This article will look at, into the Components of Computer Hardware which include all physical parts forming a computer syntactically(ARG), my focus. Knowing how these work and interact will illuminate Computer Hardware which is a lot different by being very complex yet extremely efficient at the same time.
2. The Central Processing Unit (CPU).
2.1 Definition and Function.
The Focal Preparing Unit (processor) is normally alluded to as the “mind” of the PC. It executes instructions from programs and processes data. Between managing data, the CPU would be decoded and implemented in general Computer Hardware Components which is found to manage all round functioning of your computer.
2.2 Components of the CPU.
Need of a Processor: KEY Computer Hardware Components inside the CPU.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): a machine that does the math for you and logical operation.
- Control Unit (CU): Coordinates the operations and actions in processor, controlling what memory does, calculating processes with ALU, handling inputs/ outputs devices for instruction.
- Registers:Fast, small storage locations where data and instructions are kept temporarily.
2.3 Types of CPUs.
CPUs come in various types, each designed for different performance levels:
Single-core CPUs: These handle one instruction at a time and are suitable for basic tasks.
Multi-core CPUs: These have multiple processing units that can manage several instructions simultaneously, improving performance for complex tasks and multitasking.2.4 CPU Performance.
The performance of a CPU is influenced by several factors:
Clock Speed: Measured in GHz, this indicates how many cycles per second the processor can execute.
Core Count: More cores can enhance performance by allowing multiple tasks to be processed at the same time.
Cache Memory: This is a small, fast memory located on the processor that stores frequently accessed data, reducing the time needed to retrieve this information from the main memory.
3. Memory: RAM and ROM.
3.1 Random Access Memory (RAM).
RAM is a type of volatile memory that temporarily holds data and instructions that the computer’s processor needs while executing tasks. When the computer is powered off, the information in RAM is lost. The more RAM a computer has, the more data it can handle simultaneously, which enhances performance.
3.2 Read-Only Memory (ROM).
ROM is a type of non-volatile memory that permanently stores essential data and instructions required for the computer to start up and perform basic functions. Unlike RAM, the information in ROM is retained even when the computer is turned off.
3.3 Differences Between RAM and ROM.
- Volatility: RAM is volatile, meaning it requires power to maintain the stored data, while ROM is non-volatile.
- Purpose: RAM is used for temporary data storage and quick access by the processor, while ROM holds permanent data necessary for booting and fundamental operations.
4. Storage Devices.
4.1 Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
The hard disk drive is the traditional kind of storage device; it depends on spinning disks with a magnetic coating to store data. They can offer big capacities at comparably low prices; however, they are usually slower in comparison with new storage technologies.
4.2 Solid State Drive (SSD).
The SSD store data using flash memory. It has quicker reading and writing data access compared to the HDD. Besides, being without mobile parts, it is also more resistant and consumes less energy.
4.3 Hybrid Drives.
Hybrid drives retain great storage capacity from HDDs and combine that with speed similar to that of SSDs, making a good compromise between performance and price.
4.4 External Storage.
This offers additional storage capacity and the convenience for users who find transferring data from one computer to another much easier by using USB flash drives or external hard.
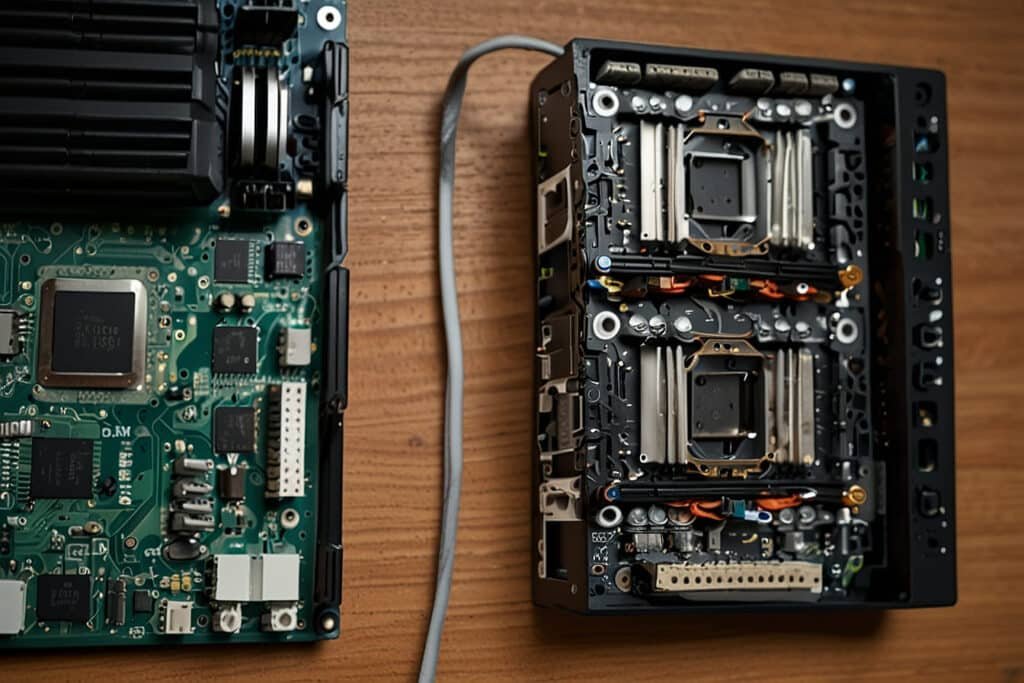
5. Motherboard.
5.1 Definition and Function.
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer, wherein other parts are connected to enable such parts to work with each other. It houses the CPU, memory, storage devices, and every other major Computer Hardware Components that enables the general operation of the computer.
5.2 Key Computer Hardware Components on the Motherboard.
- CPU Socket: Secures the CPU and links it to other Computer Hardware Components.
- RAM Slots: Provide spaces for RAM modules.
- Chipset: Controls data flow between the CPU, memory, and other peripherals.
- Expansion Slots: Allow for the addition of extra components, such as graphics cards and sound cards.
- Connectors and Ports: Enable connections to external devices, including USB ports, audio jacks, and network ports.
5.3 Form Factors.
Motherboards come in various form factors, which determine their size and compatibility with computer cases and Computer Hardware Components:
- ATX:A popular form factor for desktops, offering a good balance between expandability and size.
- Micro-ATX: A more compact version of ATX, designed for smaller systems.
- Mini-ITX: A very small form factor perfect for space-saving and portable PCs.
6.Power Supply Unit (PSU).
6.1 Definition and Function.
The PSU converts power from an outlet into usable energy for the PC’s components. It ensures that each hardware component receives the correct amount of power, protecting them from damage caused by power surges or shortages.
6.2 Types of PSUs.
- Modular PSUs: Allow users to connect only the cables they need, reducing clutter and improving airflow within the case.
- Non-modular PSUs: Come with fixed cables, which can create more mess but are often more budget-friendly.
6.3 Power Ratings.
PSUs are rated by their maximum power output, measured in watts. Choosing a PSU with the right power rating is essential for ensuring the computer operates efficiently and reliably.
7. Input Devices.
7.1 Keyboard.
The keyboard is a key input device used for typing text and commands into a computer. There are many different designs and styles available, including ergonomic and mechanical keyboards.
7.2 Mouse.
The mouse is another essential input device that allows users to navigate the computer’s graphical user interface. Mice can be wired or wireless and come with various features, such as additional buttons and adjustable sensitivity settings.
7.3 Other Input Devices.
- Touchscreen: This device lets users interact directly with the screen by touching it.
- Trackpad: A touch-sensitive area typically found on laptops, serving as an alternative to a mouse.
- Game Controllers: These are specifically designed for gaming, offering unique input options for a more immersive experience.
8. Output Devices.
8.1 Monitor.
The monitor is the main output device, displaying visual information from the computer. Monitors are available in various sizes, resolutions, and technologies, including LCD and LED.
8.2 Printer.
Printers create physical copies of digital documents and images. Common types include inkjet, laser, and multifunction printers.
8.3 Speakers and Headphones.
Speakers and headphones output sound from the computer, delivering audio for various applications, from music and videos to gaming and communication.
9. Peripheral Devices.
9.1 External Storage.
External storage devices offer extra storage capacity and can be utilized for backing up and transferring data.
9.2 External Graphics Cards.
External graphics cards can enhance the visual performance of workstations and various PCs that have limited internal graphics capabilities.
9.3 Other Peripherals.
- Webcams: Provide video input for video conferencing and streaming.
- Microphones: Catch sound for correspondence, recording, and different applications.
10. Computer Hardware Components Networking Hardware.
10.1 Network Interface Card (NIC).
The NIC enables a computer to connect to a network, facilitating communication with other devices. NICs can be wired (Ethernet) or remote (Wi-Fi).
10.2 Routers and Switches.
Switches and switches oversee information traffic inside an organization, guaranteeing productive and secure correspondence between gadgets.
10.3 Modems.
Modems interface a PC to the web by changing over computerized information into a configuration reasonable for transmission over telephone lines or link frameworks.
11. Conclusion.
Understanding the basic Computer Hardware Components of a computer is fundamental for anyone interested in technology. Each component plays a vital role in the overall operation of the system, and advancements in hardware continue to drive the capabilities of modern computers. By familiarizing yourself with these Computer Hardware Components, you can make informed decisions when building, upgrading, or troubleshooting a computer, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.

